Share This Article
First appearing last January in Wuhan, China, the COVID-19 outbreak continues to spread to more than 200 countries, including Indonesia. In early October, the worldwide death toll reached one million.
The ongoing pandemic has changed many aspects of life, such as the habit of wearing masks. On the other hand, scientists are constantly trying to develop a vaccine for the disease.
Let’s find out more information about COVID-19 with the following review!
What is COVID-19 disease?
COVID-19 is a disease caused by a viral infection. COVID-19, which stands for Coronavirus Disease 2019 , is a disease that attacks and affects the respiratory tract, especially the lungs.
The disease is highly contagious, as the virus that triggers it can be spread through the air. Transmission from person to person makes COVID-19 cases continue to increase day by day.
In severe cases, a person can experience a variety of serious complications that can be life-threatening.
What causes COVID-19?
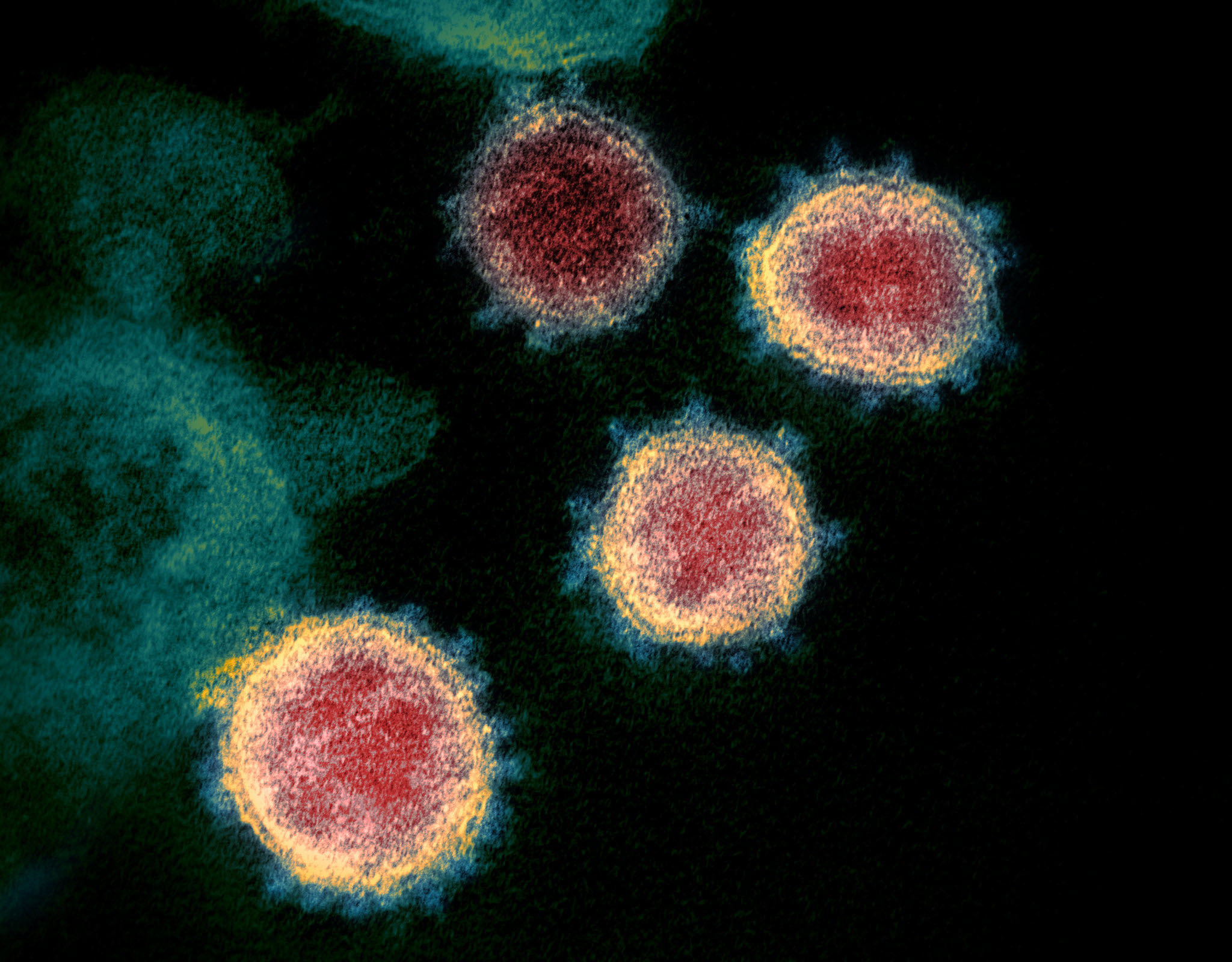
The main cause of COVID-19 is SARS-CoV-2, a type of coronavirus. This is not the first time a virus of this genus has caused an outbreak. There have been a number of outbreaks of the same virus, one of which was Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) in 2012.
The World Health Organization WHO explained that Corona is a zoonotic virus. This means that the virus first developed in animals before being transmitted to humans.
Once the person is infected, the virus can migrate to other people(human-to-human). Once the virus develops in the human body, SARS-CoV-2 can spread to others throughdroplets when sneezing, talking or coughing.
Who is more at risk of COVID-19?
Everyone has a chance of contracting the coronavirus. However, there are some groups that have a higher risk, including:
- Living with someone who has been infected
- Directly involved in the management of COVID-19 disease
- Traveling far, especially to a place with high cases
- Gathering and meeting with people who have been infected.
To date, scientists continue to conduct research on this transmission pattern. A person who already has certain diseases or conditions is also believed to be more susceptible to infection with the Corona virus, such as:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disorders
- Obesity
- Inflammation of the lungs
- Diabetes
- Liver disorders.
What are the symptoms and characteristics of COVID-19?
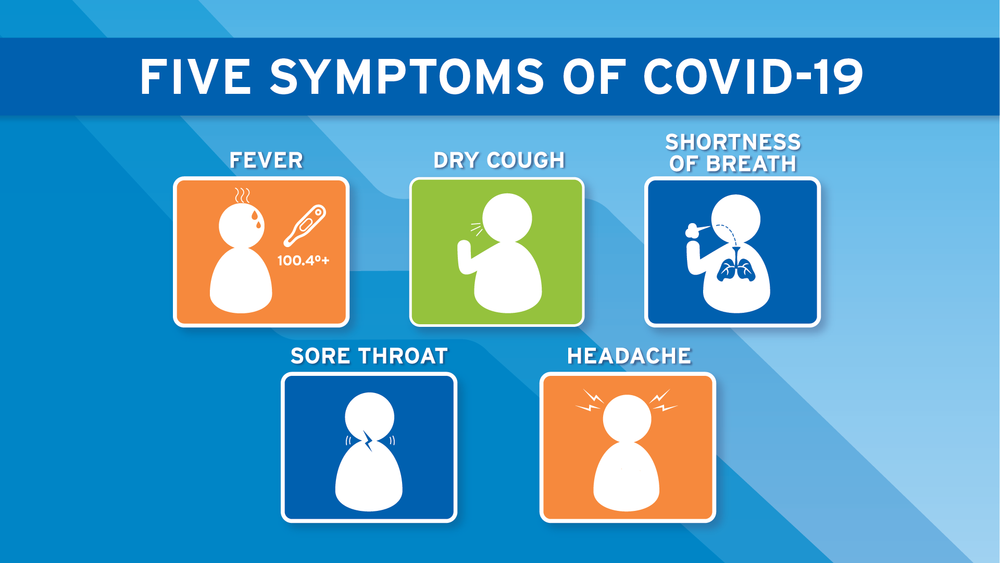
Symptoms of a disease will appear when the triggering virus or bacteria has infected the body. In the case of COVID-19, symptoms can appear as early as 14 days after initial exposure to the virus. This refers to the incubation period of SARS-CoV-2 itself.
Fever is one of the most common symptoms. When this happens, the immune system is trying to fight off the virus. Other symptoms that can appear afterward include:
- Cold heat
- Dry cough
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Chills
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Loss of smell or taste
- Nausea
- Diarrhea.
According to the Ministry of Health, the clinical symptoms of the disease can be observed from day to day with the following phases:
- Day 1: A person infected with the coronavirus will experience fever, fatigue, and a dry cough. Some experience diarrhea and nausea in the stomach.
- Day 5: Shortness of breath started to occur. This condition is particularly susceptible in older people or those with a history of other diseases.
- Day 7: This is the average time patients enter the hospital for treatment.
- Day 8: Patients develop more severe conditions, such as acute respiratory distress. The lungs have filled with fluid and can be fatal.
- Day 10: When symptoms worsen, the patient will be taken to the ICU. At that time, a small percentage of patients may die.
- Day 17: After being hospitalized for more than two weeks, the patient’s condition gradually improved. If the test result is negative, the patient is discharged.
Asymptomatic cases
Not everyone who is infected will show symptoms. This group is referred to as asymptomatic, asymptomatic people (OTG), or asymptomatic confirmed cases.
The risk of spreading the virus from an OTG to a regular patient is no different. This has caused concern among many. Asymptomatic can make a person unaware that they are infected and pass it on to others.
According to an Italian study, most OTG cases are found in young people. Unlike older people, young people are believed to have a stronger immune system. So, the body can be more optimal in fighting foreign substances that enter, including the Corona virus.
In fact, asymptomatic cases are not symptom-free. OTG still has symptoms, but not at the beginning of time. Asymptomatic symptoms last longer, from 24 days to nearly a month post-infection.
Read also: Corona cases without symptoms are found, what are the characteristics?
What are the possible complications of COVID-19?
If properly treated, a person infected with the coronavirus without a history of other serious illnesses is very likely to recover. On the other hand, the situation can worsen if the patient does not receive immediate treatment, especially if they have a congenital disease.
Some serious complications of COVID-19 include:
1. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammation that occurs in the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli). Usually, this complication occurs when the coronavirus manages to expand and reach many parts of the lungs.
Pneumonia can cause death. Oxygen cannot be properly absorbed into the blood to be distributed throughout the body because the air sacs are filled with fluid due to inflammation.
2. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is the most common complication. Quoting WebMD, this complication affected many Chinese citizens at the beginning of the outbreak.
A person with ARDS will have difficulty breathing. This condition is caused by a buildup of fluid in the alveoli due to damaged and leaky capillaries in the lungs. The damage to these vessels is the result of other severe diseases, including COVID-19.
A person with ARDS is usually treated using a ventilator to keep breathing.
3. Sepsis
Sepsis is the most severe complication, usually preceded by pneumonia. This condition can occur when the triggering virus successfully spreads through the bloodstream, causing damage to every tissue it passes through.
According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, sepsis can have a serious impact on cardivascular organs such as the heart. The biggest risk is death. Even if they survive, the patient will have permanent damage to the lungs and other important organs.
4. Blood clots
A lesser-known complication is blood clots. This condition has affected one-third of patients admitted to the ICU. Blood clots can occur in the legs(deep vein thrombosis), lungs(pulmonary embolism), or arteries.
Read also: 10 Complications that Can Occur When Infected with COVID-19
How to overcome and treat COVID-19?
There are two types of treatment for positive patients, namely hospitalization and self-isolation at home.
COVID-19 treatment in hospital
Before being diagnosed with coronavirus, you will undergo a series of tests. In Indonesia, the most commonly used tests arerapid tests and PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests.
The rapid test requires a blood sample to detect the presence of Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin M antibodies. Immunoglobulin G is an antibody that stores ‘traces’ of past infections. That way, the immune system can provide protection in the future from the same infection.
Immunoglobulin M is the first antibody produced by the immune system once a virus or bacteria has successfully infected. These antibodies will form on their own after a viral or bacterial infection manages to enter your body.
If the rapid test shows a reactive result, you will be directed to do a follow-up test, the PCR test. This test aims to detect the genetic material of the coronavirus.
Isolation room
All coronavirus positive patients must be treated in isolation. The treatment must also follow the standard health protocols that have been established. For example, every doctor and medical personnel must use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as hazmat and N95 masks.
Ventilator use
During a pandemic, the presence of ventilators or breathing apparatus in hospitals is very important. Not all patients need this device, but only those with symptoms of shortness of breath and serious complications as described earlier.
Read also: Important! This is the Difference between PCR Test and COVID-19 Rapid Test that You Should Know
How to treat COVID-19 naturally at home
Treatment of positive cases at home is aimed at people who are asymptomatic or OTG. This is because there are no complaints that must be treated medically.
Self-isolation aims to suppress the spread of the virus from infected people. What you can do is keep eating nutritious foods to boost your immune system, and maintain hygiene by washing your hands frequently.
What are the commonly used COVID-19 medications?
Quoting the Mayo Clinic, there is no drug that can really overcome this disease. Researchers are also testing various possible treatments.
COVID-19 medication at pharmacies
Although there are many antiviral drugs, their effectiveness in treating COVID-19 is still in doubt. Some countries, including the United States, are using antivirals like remdesivir to kill the coronavirus.
For treatment in most hospitals, the treatment process focuses on the patient’s symptoms, such as using painkillers like acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
Natural COVID-19 cure
Until now, there has not been a single study that explains the effectiveness of herbs in handling COVID-19. In some countries, including Indonesia, herbs are used to boost the immune system, not to treat COVID-19 itself.
Last August, the Indonesian Institute of Sciences (LIPI) completed clinical trials on an immunomodulator made from a combination of herbs. In addition to boosting the immune system, the immunomodulator is expected to help relieve symptoms in positive patients.
Some herbs and spices that are believed to boost the body’s immune system include ginger, cloves, cinnamon, sambiloto leaves, and lemongrass.
Read also: The Pandemic Has Not Ended Drinking Wedang Uwuh Don’t Stop, Here are 7 Benefits
What are the foods and restrictions for people with COVID-19?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are no specific recommendations or restrictions for positive patients. This is because this disease does not come from food, but a virus. What must be considered is the hygiene aspect of the food itself.
To boost your immune system, you can consume nutritious foods that are rich in vitamins, such as fresh fruits and vegetables.
How to prevent COVID-19?

To date, there is no effective way to prevent the transmission of the coronavirus. Scientists in many countries are developing vaccines to prevent the virus.
What can be done is to minimize the potential for transmission, namely by implementing health protocols according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), such as:
- Always clean your hands with soap and water frequently. If traveling, bring an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with you.
- Keep a safe distance of at least one meter from anyone, especially people who are coughing and sneezing.
- If there is no urgent business, stay at home.
- If you must go outside, always wear a cloth mask.
- Do not touch your eyes, nose and mouth with your hands. There could be a virus attached to your hands.
- Cover your nose and mouth with your bent elbow or a tissue if you cough or sneeze.
- If you feel sick, stay home and limit your contact with people.
- If the high fever is accompanied by coughing and difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical attention from the nearest health facility. Consider using the phone first to contact the hospital and follow the instructions given.
Vaccines for COVID-19
Vaccines are necessary to prevent COVID-19 transmission. Unfortunately, according to the WHO, it is almost certain that there will be no vaccine for COVID-19 this year, but from mid-2021.
As of early October, there are at least 42 types of vaccine candidates that have entered the clinical evaluation stage. These vaccines are produced by several pharmaceutical companies in a number of countries, including:
- Sinovac (China)
- Sinopharm (China)
- AstraZeneca (University of Oxford)
- Moderna (United States)
- Dynavax (China)
- Seqirus (Australia)
- SpyBiotech (India)
- CanSino (China)
- BioNTech (Germany)
- AnGes (Japan)
- Medytox (South Korea)
Well, that’s a review of COVID-19 and the symptoms that accompany it. Let’s adhere to health protocols to minimize and break the chain of the spread of the Corona virus. Stay healthy!
Consult your and your family’s health problems through Good Doctor in 24/7 service. Our physician partners are ready to provide solutions. Let’s download the Good Doctor app


